
In conventional designs, non-client router will be route reflector for routers in the next hierarchy level but in this example just another PE is used for simplicity. In this case, S1PE1 and S1PE2 are clients of RR while S2PE1 is non-client. Neighbor 10.0.20.2 route-reflector-client Neighbor 10.0.10.2 route-reflector-client Single Cluster with Default Settingsįollowing configuration has been done on router RR acting as route reflector.
#Route reflector update#
This attribute is used for loop prevention: when router receives update which CLUSTER_LIST contains router's own cluster ID, this update is discarded.īy default cluster ID is set to the BGP router id value, but can be set to an arbitrary 32-bit value. When route reflector reflects a prefix, it creates/modifies an optional non-transitive attribute called CLUSTER_LIST by adding its own cluster ID to it.
#Route reflector full#
RFC4456 introduces the route reflection feature which removes the need of full mesh between iBGP speakers. By default BGP speakers does not advertise iBGP-learned prefixes to iBGP peers - this is done to maintain loop prevention. Description of BGP Route ReflectionĪ BGP speaker is a BGP enabled router.
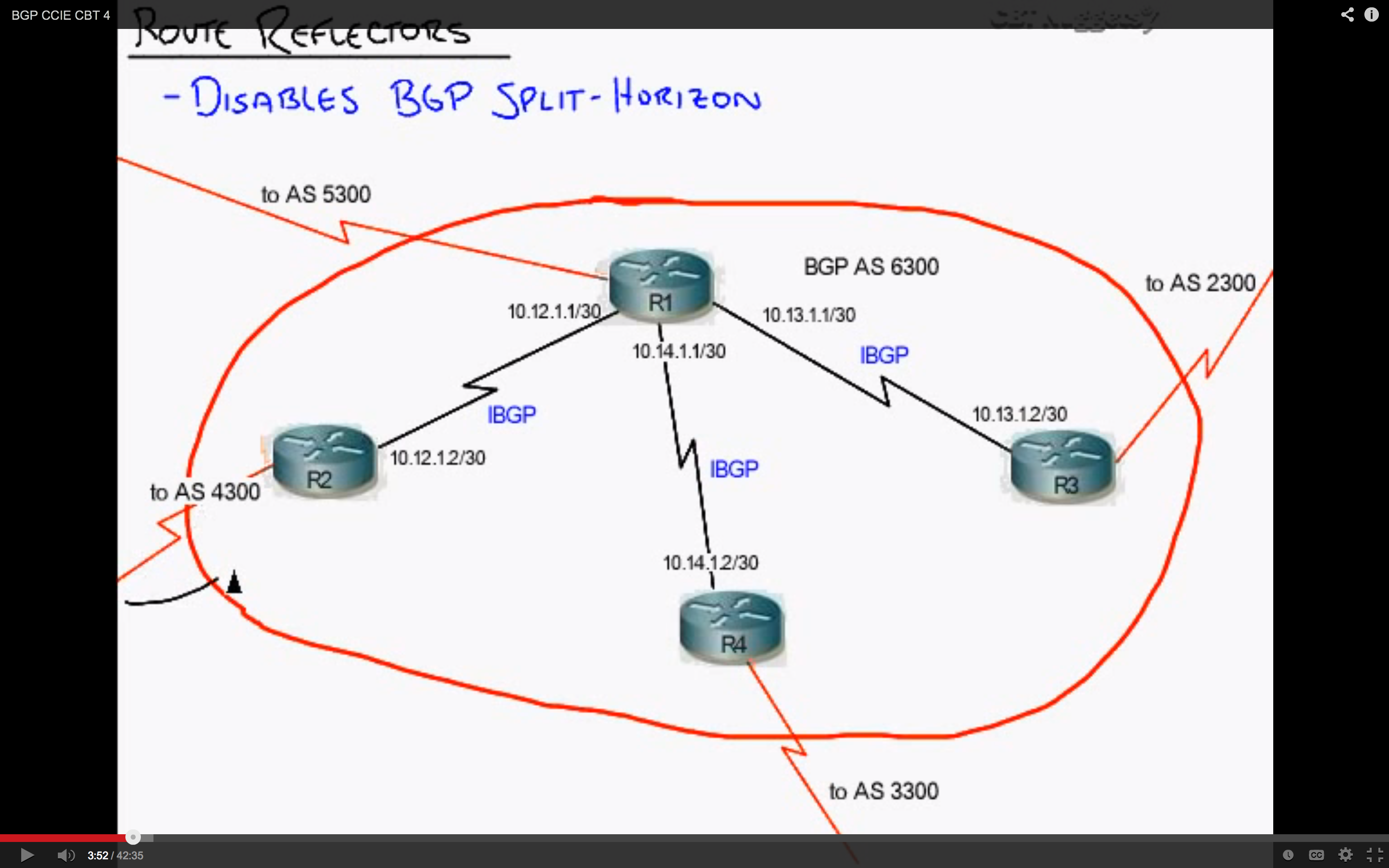
Prior knowledge of BGP concepts especially clusters and route reflection is assumed. Infrastructures with route reflectors in place, be it of any configuration, can now use Noction IRP to reroute traffic across multiple ISPs based on critical performance metrics and achieve considerable reduction in packet loss, latency and network downtime.This article describes different scenarios of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) route reflection and usage of multiple cluster IDs. Bellow is a diagram depicting the IRP configuration within a topology that uses route reflection. IRP can now announce routing updates to a route reflector that further propagates them to the edge routers. RR1, in turn, distributes the routes among the Level 2 reflectors that further propagate the routes down their clusters.įigure 3: Hierarchical configuration of route reflectorsĪs route reflection is a concept frequently used in various network configurations, we have added full support of route reflectors in Noction IRP 2.1. All the routes advertised to RR2 will be readvertised within Cluster 2 and then, readvertised to RR1. Rather than fully mesh these reflectors they can be grouped in a separate cluster for which RR1 will be the route reflector. In Figure 3, RR2 and RR3 are route reflectors for Cluster 2 and Cluster 3 respectively. These, in turn, readvertise the routes to their clients.įigure 2: Configuration of route reflectors in multiple clusters When a router advertises to RR1, RR1 further distributes the routes to the rest of route reflectors. RR is configured as a route reflector redistributing routes among the connected internal peers.įigure 1: Single cluster route reflector configurationĪs shown in Figure 2, you can have multiple clusters with the route reflectors configured as fully meshed internal peers. You simply establish a BGP session from the route reflector to each internal peer and the iBGP full-mesh requirement is met.įigure 1 shows the configuration of a single cluster with one route reflector. A route reflector is not limited by the re-advertising restriction anymore, allowing it to share routes with other iBGP speakers. Using the route reflection principle you can designate one or several of your routers as route reflectors. iBGP neither has any loop prevention mechanism, and this is why you require route reflectors to be setup for large networks.
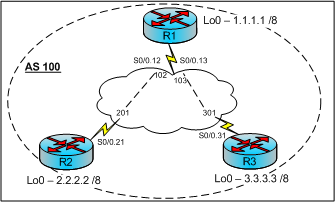
Because of that, the routers should be fully interconnected, hence the full mesh requirement. IBGP has the restriction of not allowing to redistribute the learned routes to other internal peers.
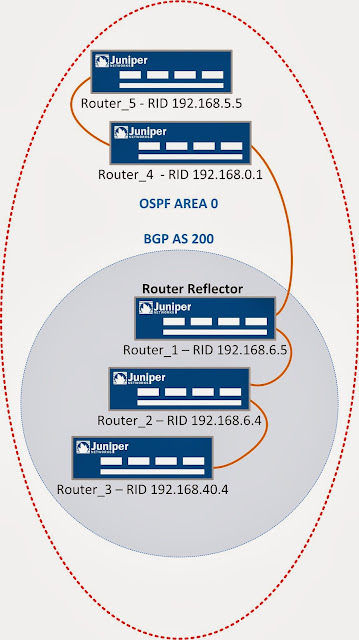
Route reflection enables sharing of routing information among multiple routers without having to send the exact same information to each of them individually. Route reflection comes to solve the complexity of multiple peering configuration. Therefore, in a large network, the full-mesh requirement for iBGP can be a big challenge. Because of the increasing numbers of iBGP sessions the possibilities of scaling are limited. The typical fully-meshed iBGP configuration of routers can become very difficult to manage in large networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
